WHAT IS POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME (PCOS)?
WHAT IS POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME (PCOS)
PCOS is a condition that can affect.
- Your periods.
- Your fertility.
- Aspects of your appearance.
- Long term health.
HOW COMMON IS THE CONDITION?
Estimates vary from 2 to 26 in every 100 women.
Symptoms of PCOS
- Irregular periods.
- An increase in facial or body hair.
- Loss of hair on your head.
- Being overweight/experiences a rapid increase in weight /having difficulty losing weight.
- Oily skin, Acne.
- Infertility (difficulty in conceiving).
- Depression and psychological problems can also result from having PCOS.
- Symptoms vary from women to women from mild to severe.
What causes PCOS ?
The cause of PCOS is not yet known. There is a proven insulin resistance.
It often runs in families.
The Symptoms are Related to Abnormal Hormone Levels.
- Testosterone is a hormone that is produced in small amounts by the ovaries in all women. Women with PCOS have slightly higher than normal levels of testosterone and this is associated with many of the symptoms to the condition.
- Insulin is a hormone that controls the level of glucose in the blood. If you have PCOS, your body may not respond to insulin (this is known as insulin resistance) so the level of glucose is higher.
- To try to prevent the glucose levels becoming higher, your body produces even more insulin.
- High levels of insulin can lead to weight gain, irregular periods, fertility problem and higher levels of testosterone.
How is PCOS Diagnosed?
A diagnosis is made when you have any two of the following.
- Irregular, infrequent periods or no periods at all.
- An increase in facial or body hair and/or blood tests that show higher testosterone levels than normal.
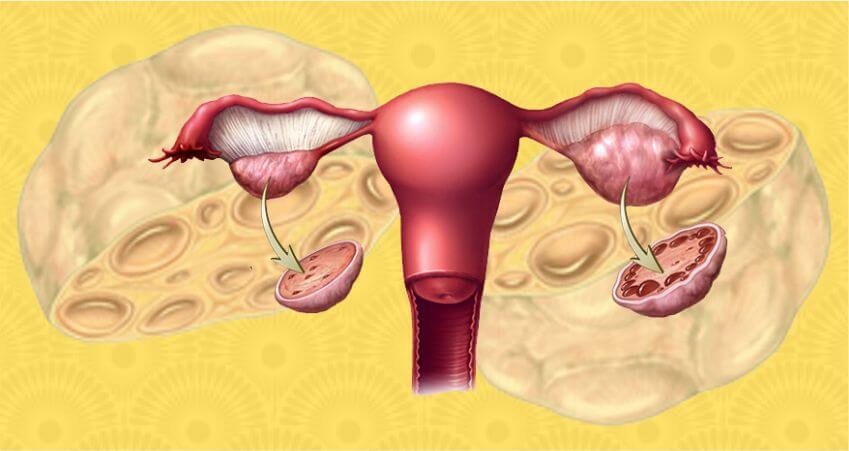
- An ultrasound scan that shows polycystic ovaries.
Management of PCOS
The Principal Components of Management
- Eat a healthy balanced diet this should include fruit and vegetables and whole foods (such as brown rice, whole wheat bread, lean meat, fish and chicken.)
- You should cut down the amount of sugar, salt and caffeine that you eat and drink.
- Take exercise regularly(30 mts at least 3 times a week)
- If you are overweight it would be helpful to lose weight and maintain body mass index (BMI)between 19 and 25.
(BMI is the measurement of weight in relation to height.)
The Benefit of Reducing Weight Include
- A lower risk of insulin resistance and avoid develop diabetes.
- A lower risk of heart problems.
- A lower risk cancer of the womb.
- More regular periods.
- An increased chance of becoming pregnant.
- A reduction in acne and decrease in excess hair growth over time.
- Improve mood and self esteem.
- To regularize irregular periods, consult your gynaecologist.
- Management of infertility needs specialist intervention.
- Skin specialist/dermatologist can help managing acne excess facial/ body hair growth and oily skin.
Management of PCOS Control
- HAVE REGULAR HEALTH CHECKS: Once you have a diagnosis of PCOS, you need to be monitored for long term health problems.
- DIABETES: Women with PCOS over the age of 40 should be offered a blood sugar test once a year to check for signs of diabetes.
- CANCER OF THE WOMB: If you have not had periods for a long time (over 4 months) or have irregular bleeding, it is advisable to see your doctor.
- High blood pressure, routine health checks with your physician should keep it under check.
- Depression and psychological problems can occur due to various factors and needs to be handled.
IS THERE A CURE?
There is no cure for PCOS
Medical treatments aim to manage and reduce the symptoms or consequences of having PCOS.
Medication alone has not been shown to be any better than healthy lifestyle changes.